India’s school education system is undergoing a quiet revolution—one rooted in equity, inclusion, and a deep understanding of diverse learning needs. The name of that revolution? Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (समग्र शिक्षा अभियान).
Launched as an integrated initiative under the Ministry of Education, Samagra Shiksha blends policy with ground-level action, reshaping how schools function and how children learn. From anganwadi centers in rural Bihar to senior secondary schools in Mumbai’s suburbs, this scheme touches them all.
At the heart of समग्र शिक्षा lies a single promise: quality education for all—regardless of background, ability, or location.
The Vision Behind Samagra Shiksha
The scheme takes its cue from two pillars—SDG 4 and the NEP 2020. Together, they lay out a path toward inclusive, equitable, and skill-oriented education.
शिक्षा सभी के लिए – Not just a slogan
Every child—whether in a tribal hamlet of Odisha or an urban slum in Delhi—deserves not just schooling, but meaningful learning outcomes. That’s what समग्र शिक्षा sets out to achieve.
A classroom that adapts to the learner
No more one-size-fits-all. The focus is now on:
- Multilingual teaching
- Culturally relevant content
- Tailored support for learners with different academic levels
Seamless education from preschool to Grade 12
Schooling isn’t chopped into disconnected segments anymore. समग्र शिक्षा sees it as a continuum—five stages, one flow.
Scheme Structure: The 5+3+3+4 Model Explained

Samagra Shiksha supports India’s new school structure introduced under NEP 2020. This structure redefines schooling phases:
| Stage | Grades | Key Approach |
| Foundational | Anganwadi – Grade 2 | Play-based, multilevel learning |
| Preparatory | Grades 3–5 | Discovery and interaction |
| Middle | Grades 6–8 | Experiential, integrated learning |
| Secondary | Grades 9–12 | Critical thinking, flexibility |
Each stage is tailored to cognitive growth, ensuring smooth transitions and stronger outcomes.
Objectives of समग्र शिक्षा: Policy Meets Practice
How does a policy document become a real-world transformation? Through clear, measurable goals — and Samagra Shiksha has many:
Implement NEP 2020 across all states
Align curriculum, training, and exams with the National Education Policy.
Strengthen foundational literacy & numeracy
Boost basic reading and math skills for early-grade learners via targeted interventions.
Ensure equity and inclusion
Special provisions for:
- Girls and transgender students
- Children with disabilities
- Marginalized communities
Upgrade institutions like SCERTs & DIETs
Equip teacher education bodies with tools, training, and digital platforms.
Promote vocationalisation of education
Introduce work-linked learning early, not just at the senior secondary level.
Coverage That Spans the Nation

The numbers behind समग्र शिक्षा are staggering:
- 1.16 million schools
- 156+ million students
- 5.7 million teachers
- Spanning pre-primary to senior secondary
And this isn’t limited to just government staff—it includes volunteers, community committees, resource persons, and parents too.
Classroom to Community: A Holistic Ecosystem
What makes Samagra Shiksha stand out is how it redefines who’s involved in education. It’s no longer teacher + textbook. It’s everyone:
Who are the stakeholders?
- Students, obviously
- Teachers and headmasters
- Parents and guardians
- School Management Committees (SMCs)
- State Councils (SCERTs, DIETs)
- Block & Cluster resource coordinators
Why this matters
When everyone is part of the ecosystem:
- Accountability increases
- Cultural fit improves
- Local ownership of reforms grows
Challenges Addressed by समग्र शिक्षा
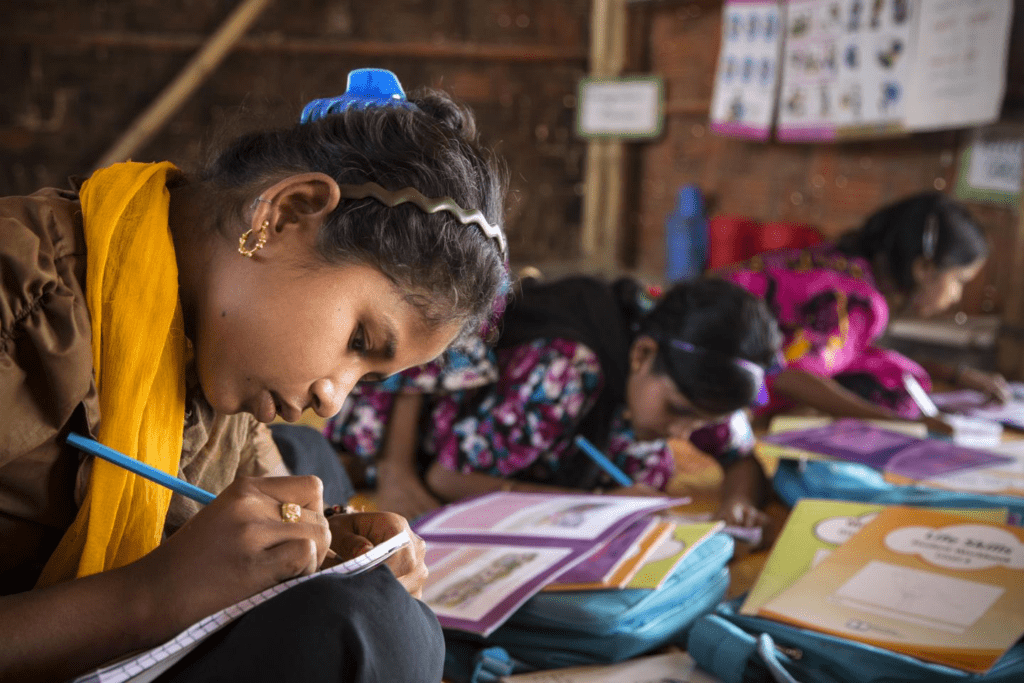

India’s schooling system faces complex issues—some visible, some silent. This mission targets all of them.
1. Bridging gender gaps
Girls still face dropout risks post-primary. समग्र शिक्षा offers safe transport, gender-sensitive toilets, and targeted scholarships.
2. Supporting remote regions
Special norms for areas like Ladakh, northeast hills, and tribal belts—flexible calendars, mobile schools, and bilingual materials.
3. Digital inclusion
E-content, smart classrooms, and DIKSHA integration for tech-based learning—even in places without stable internet.
4. Teacher empowerment
From regular training to performance-based monitoring, teachers are placed at the center—not the sidelines.
Aligning with SDG-4: Global Commitments, Local Action
Samagra Shiksha isn’t just Indian policy—it’s a piece of the global puzzle.
SDG 4.1: Quality primary and secondary education
By 2030, ensure every child completes free and effective schooling.
SDG 4.5: Eliminate gender and equity gaps
Promote access for all — including girls, differently-abled children, and vulnerable groups.
Governance and Funding: How Samagra Shiksha Is Implemented
Turning a national vision into classroom reality requires coordination across layers of government. Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan operates through a shared-responsibility model where the Centre and States work as partners, not silos.
At the policy level, annual plans are prepared by States and Union Territories based on local needs—teacher shortages, infrastructure gaps, or learning outcomes. These plans are then appraised and funded through a transparent mechanism that links resources to outcomes.
Centre–State partnership in action
Funding follows a cost-sharing pattern, ensuring both accountability and flexibility. States are encouraged to innovate while aligning with national priorities such as samagra shiksha goals and NEP 2020 benchmarks.
Monitoring without micromanagement
Instead of rigid control, the scheme emphasizes:
- Outcome-based monitoring
- Periodic data reviews through national dashboards
- Mid-course corrections driven by evidence
This balance allows समग्र शिक्षा to stay responsive to diverse regional realities.
Teachers at the Core: Training, Support, and Trust
No education reform succeeds without teachers. Samagra Shiksha places educators at the center of transformation, not as executors but as professionals with agency.
Continuous professional development
Teachers receive regular training on:
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN)
- Activity-based and experiential pedagogy
- Inclusive classrooms and special needs education
Digital platforms and blended models ensure reach even in remote districts.
From instruction to facilitation
The classroom role is shifting. Teachers are now encouraged to guide inquiry, foster discussion, and adapt content. This pedagogical shift is one of the most significant impacts of samagra shiksha abhiyan.
Infrastructure, Safety, and the Learning Environment
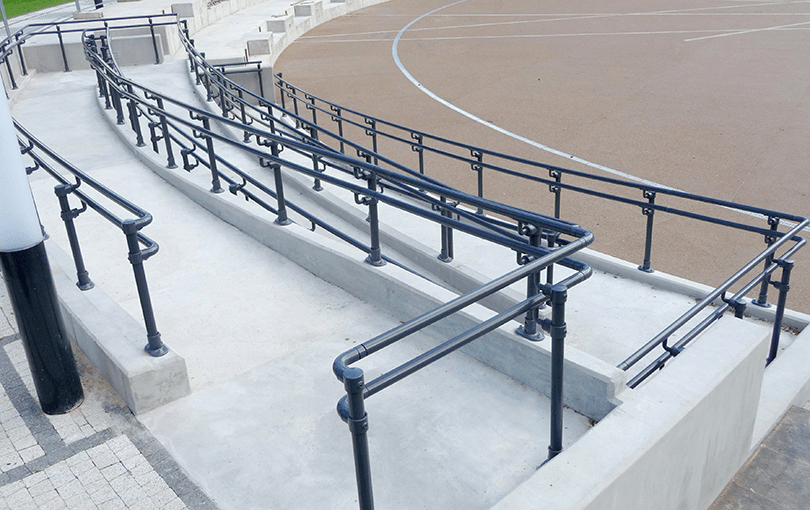

Quality learning needs safe and dignified spaces. Under समग्र शिक्षा, infrastructure is not cosmetic—it is functional and child-centric.
What schools gain
Support extends to:
- Classrooms and libraries
- Functional toilets with gender sensitivity
- Drinking water and electricity
- Ramps and assistive devices for accessibility
These interventions reduce dropouts and improve attendance, especially among girls and children with disabilities.
Vocational Education and Real-World Skills
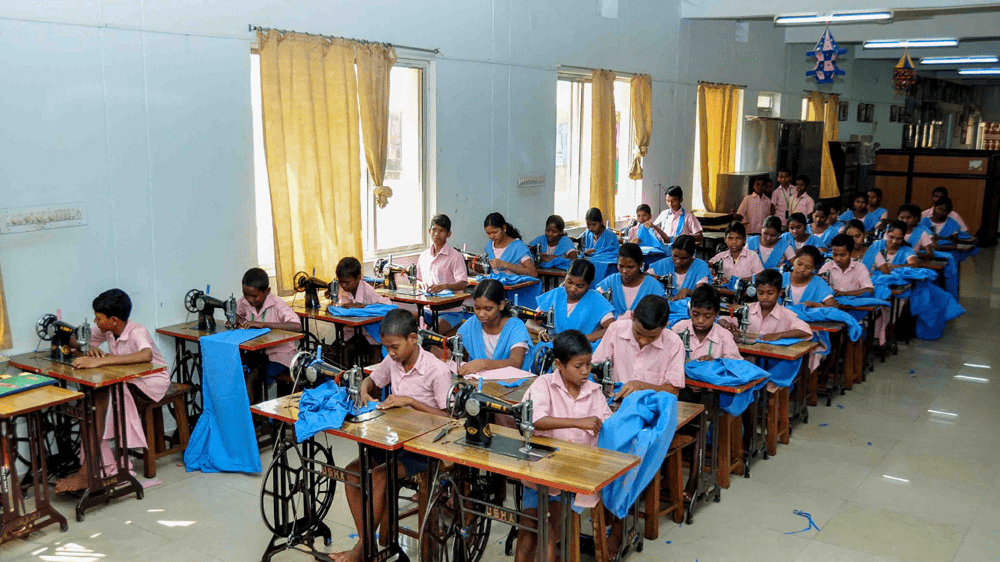

Schooling is no longer just about exams. Samagra Shiksha promotes early exposure to skills that connect learning with life.
Why vocationalisation matters
Students gain:
- Awareness of local trades and services
- Basic employability skills
- Respect for all forms of work
This shift aligns education with India’s demographic and economic realities, preparing learners for multiple pathways after school.
Measuring Impact: What Has Changed on the Ground?
After several years of implementation, patterns are emerging. While challenges remain, certain outcomes are clear.
Visible improvements
- Higher enrolment in upper primary and secondary levels
- Improved access for marginalized groups
- Stronger focus on early-grade learning
Data-driven planning has replaced guesswork, making samagra shiksha more adaptive over time.
What Lies Ahead for Samagra Shiksha
Extended through 2025–26, the scheme is entering a critical phase. The next steps will determine whether reforms deepen or plateau.
Priorities for the coming years
- Strengthening learning assessments beyond rote metrics
- Expanding digital equity without excluding offline learners
- Deeper community participation in school governance
Can India sustain this momentum and translate policy into lasting learning gains?
Why Samagra Shiksha Matters to Every Family
Whether you are a parent, teacher, or student, समग्र शिक्षा shapes daily school experiences. It influences what is taught, how it is taught, and who gets access.
This is not just a government scheme—it is a national commitment to dignity, opportunity, and learning with purpose. Education here is not preparation for life. It is life itself.

